Ludwig Mies van der Rohe was a German-American architect. He was commonly referred to as Mies, his surname. Along with Alvar Aalto, Le Corbusier, Walter Gropius and Frank Lloyd Wright, he is regarded as one of the pioneers of modernist architecture.
Mies sought to establish his own particular architectural style that could represent modern times just as Classical and Gothic did for their own eras. He created his own twentieth-century architectural style, stated with extreme clarity and simplicity. His mature buildings made use of modern materials such as industrial steel and plate glass to define interior spaces, as also conducted by other modernist architects in the 1920s and 1930s such as Richard Neutra. Mies strove toward an architecture with a minimal framework of structural order balanced against the implied freedom of unobstructed free-flowing open space. He called his buildings "skin and bones" architecture. He sought an objective approach that would guide the creative process of architectural design, but was always concerned with expressing the spirit of the modern era. He is often associated with his fondness for the aphorisms, "less is more" and "God is in the details"
Barcelona Pavilion, Spain
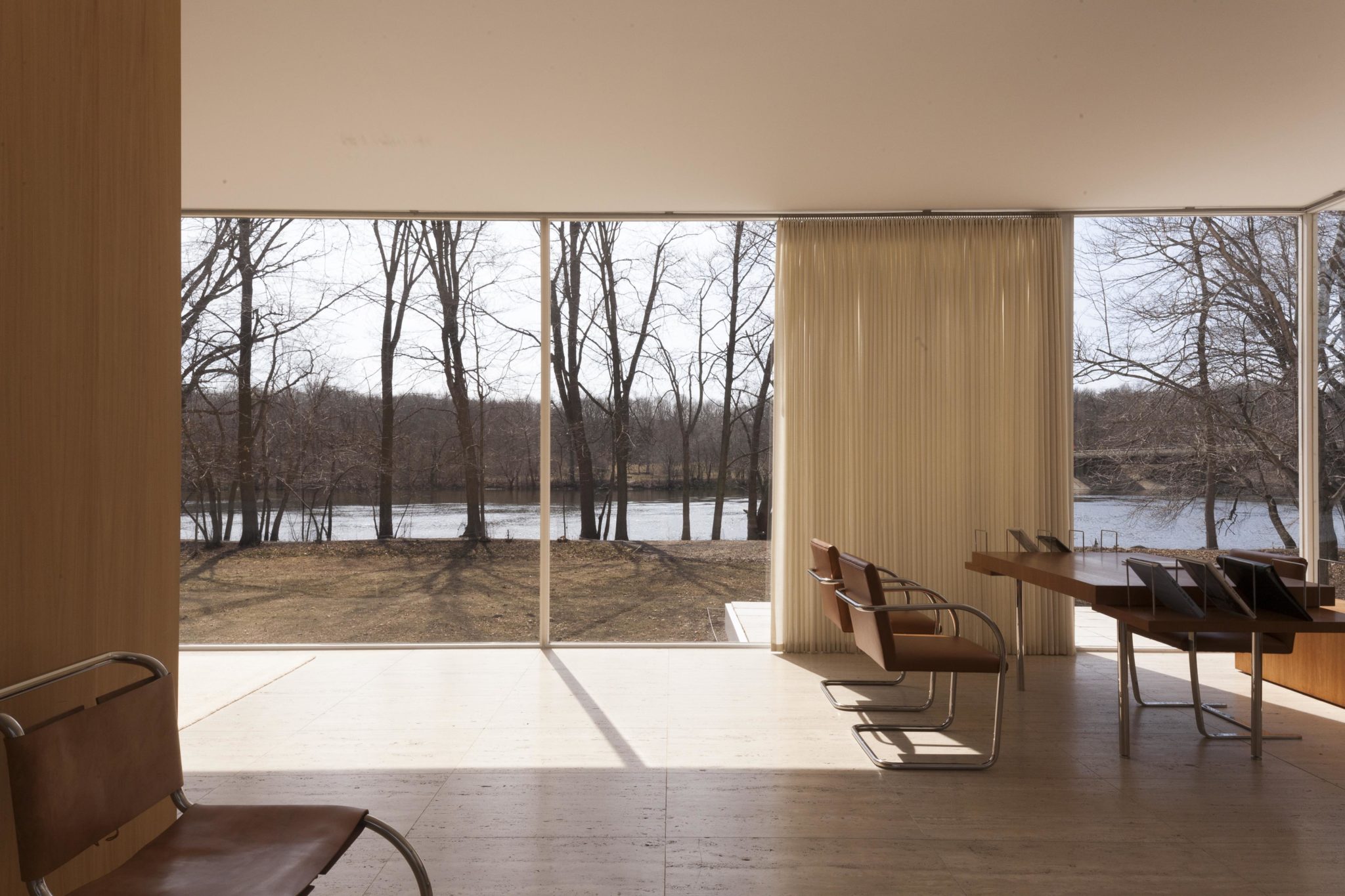
Farnsworth House, Illinois
 PHOTOS BY LIZ CHILSEN
PHOTOS BY LIZ CHILSENPhoto Categories: exterior, mid-century building type, flat roofline, house building type
Between 1946 and 1951, Mies van der Rohe designed and built the Farnsworth House, a weekend retreat outside Chicago for an independent professional woman, Dr. Edith Farnsworth. Here, Mies explored the relationship between people, shelter, and nature. The glass pavilion is raised six feet above a floodplain next to the Fox River, surrounded by forest and rural prairies.
The highly crafted pristine white structural frame and all-glass walls define a simple rectilinear interior space, allowing nature and light to envelop the interior space. A wood-paneled fireplace (also housing mechanical equipment, kitchen, and toilets) is positioned within the open space to suggest living, dining and sleeping spaces without using walls. No partitions touch the surrounding all-glass enclosure. Without solid exterior walls, full-height draperies on a perimeter track allow freedom to provide full or partial privacy when and where desired. The house has been described as sublime, a temple hovering between heaven and earth, a poem, a work of art.
The Farnsworth House and its 60-acre (240,000 m2) wooded site was purchased at auction for US$7.5 million by preservation groups in 2004 and is now owned and operated by the National Trust for Historic Preservation as a public museum. The building influenced the creation of hundreds of modernist glass houses, most notably the Glass House by Philip Johnson, located near New York City and also now owned by the National Trust.
The house is an embodiment of Mies' mature vision of modern architecture for the new technological age: a single unencumbered space within a minimal "skin and bones" framework, a clearly understandable arrangement of architectural parts. His ideas are stated with clarity and simplicity, using materials that are configured to express their own individual character.
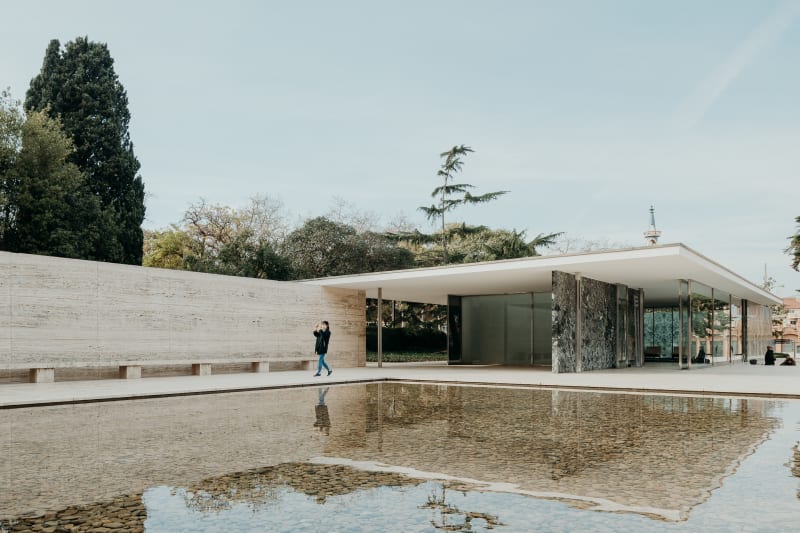 PHOTOS BY MACIEJ JEŻYK
PHOTOS BY MACIEJ JEŻYK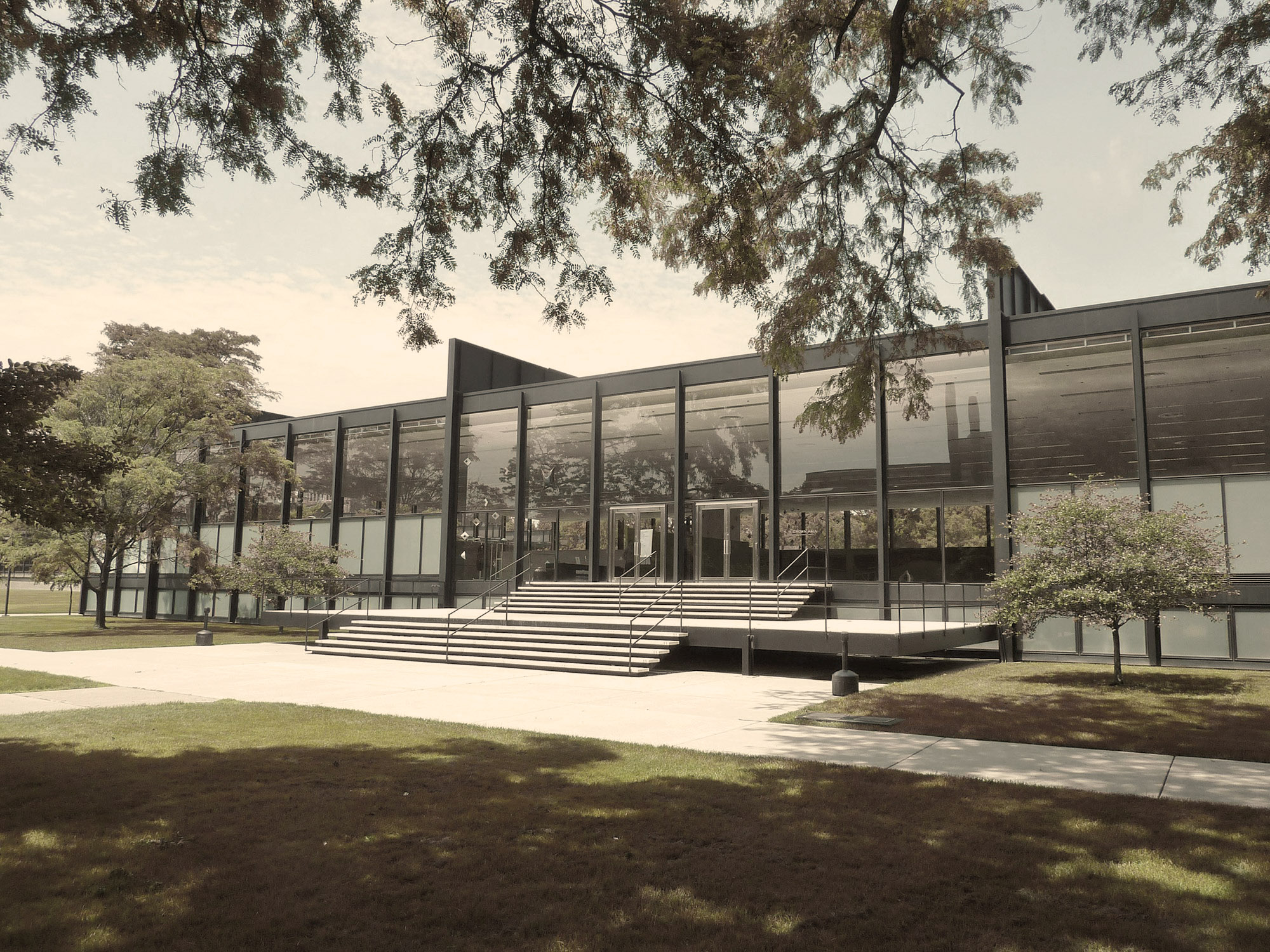 PHOTOS BY ARTURO DUARTE JR.
PHOTOS BY ARTURO DUARTE JR.